The Middle East has been building towards an AI-driven future for over a decade. 2025 is the dawn of that glorious future in the present. Previously, the development of pilot projects and innovation labs fuelled revenue, operational efficiencies, and competitive differentiation across entire organisations.

2025: The GCC’s AI Breakout Year
In the UAE, the National AI Strategy 2031 implementation phase is now heavily focused on the operation of national data platforms, sovereign AI capabilities, and cross-sector adoption. Under Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia planned millions in investments with the SDAIA, with the aim of positioning the Kingdom in the top 15 countries in the world by 2030 in terms of AI. Similarly, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, and Kuwait are massively scaling up their investments in AI across infrastructure, public services, and specific industry applications.
These remain the three major forces driving the change:
- Governance: Robust laws on AI and data protection will improve maturity among institutions so as to enable the use of intelligent advances by businesses without being bogged down in compliance paralysis.
- Infrastructure Readiness: AWS, Microsoft, Google Cloud and Oracle have recently set up their regional data centres within the GCC markets, thereby improving latency and data-residency compliance.
- Talent Acceleration: Universities and States produce AI-ready talent, while this demand from increasingly local and international sources is met through hybrid delivery models by enterprises.
Esferasoft has been a trusted partner for companies migrating from “curiosity in AI” to “AI as a core capability” with delivery hubs across India and a solid portfolio of GCC project experience. We’ve helped banks with generative AI copilots, energy firms with edge AI in hazardous environments, and public authorities launch multilingual citizen-service platforms.
The rest of this report breaks down the eight most transformative AI services and consulting trends shaping Middle East businesses in 2025 along with a pragmatic roadmap to implement them.
Executive Summary: What Changes, What Pays Off
The GCC region stands at a historic juncture in its AI journey. The considerations for investment in AI have now transitioned over the last five years from “Should we invest in AI?” to “How do we responsibly operationalise AI at scale, with measurable business outcomes?”
Three converging elements would support AI services Middle East scale-ups in 2025:
- Regulatory clarity — Governments have enacted data protection laws, AI ethics, and compliance frameworks for different sectors. Hence, CIOs and CTOs can design AI systems without second-guessing legal feasibility.
- Infrastructure maturity—Sovereign cloud zones by AWS, Microsoft, Oracle, and Google are now hosting low-latency, in-region AI workloads compliant with data residency requirements.
- AI literacy across leadership — Members of the board, CFOs, and even non-technical executives are conversant with AI value propositions, allowing faster budget approvals and smoothing the adoption.
These changes will have tangible business benefits:
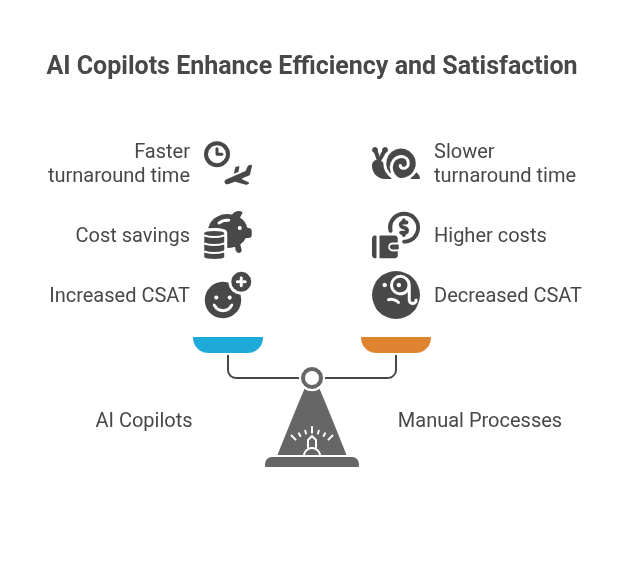
- Increased productivity is being made visible with the help of generative AI copilots: contact centres report AHTs are 20-40% faster on average and some have achieved content creation for bilingual customers 3 times faster.
- Compliance issues are reduced and multimillion-dollar private fines are avoided through data sovereignty frameworks.
- ERP modernisation and MLOps enable real-time decision-making in the supply chain, with manufacturers lowering inventory waste by 15%-18% while order fill rates are improved by 10%.
- Edge AI deployments are increasing safety and uptime in oil and gas plants, airports, and ports, with incident responses ranging from seconds to milliseconds.
- AI-driven cybersecurity saves from 30 to 50% in MTTD, allowing faster breach containment.
- Intelligent automation guarantees a 150% to 200% ROI within the first 12 months by wiping out high-volume manual workflows.
- Digital twins lengthen asset life up to 25% and diminish unplanned downtime by 40%.
- AI-driven ESG reporting is shortening compliance reporting cycles from months to weeks, thus freeing teams to concentrate on real sustainability improvements.
Strategically, what changes is that AI is no longer treated as an ad hoc technology experiment; it becomes a core operational layer embedded in ERP, CRM, and industry-specific systems. Organisations that will be winners in 2025 will be those that:
- Build AI on governed, sovereign architectures.
- Lighthouse approach—Focus first on high-value, high-visibility use cases.
- Integrate AI into everyday workflows rather than inventing separate tools.
- Treat MLOps and change management as essential enablers, not something to be considered later.
Bottom line: The Middle East is fast moving from pilots to platforms and curiosity to competitiveness—those organisations achieving scale in AI with governance and intention will reap rich rewards, both financially and strategically.
Given the Middle East Moment: Policy, Talent, and Infrastructure Tailwinds
The increase in AI usage across the GCC countries is driven by a combination of policy certainty, talent development, and high-quality digital infrastructure, creating one of the most favourable environments on earth for AI-driven transformation.
1. Policy Certainty as Catalytic
In the past three years, Middle Eastern nations have not only presented ambitious AI visions from their governments but have also established concrete frameworks and regulations. This has eliminated the uncertainty that can otherwise slow down acceptance of enterprises in other markets.
National AI Strategies with measurable KPIs
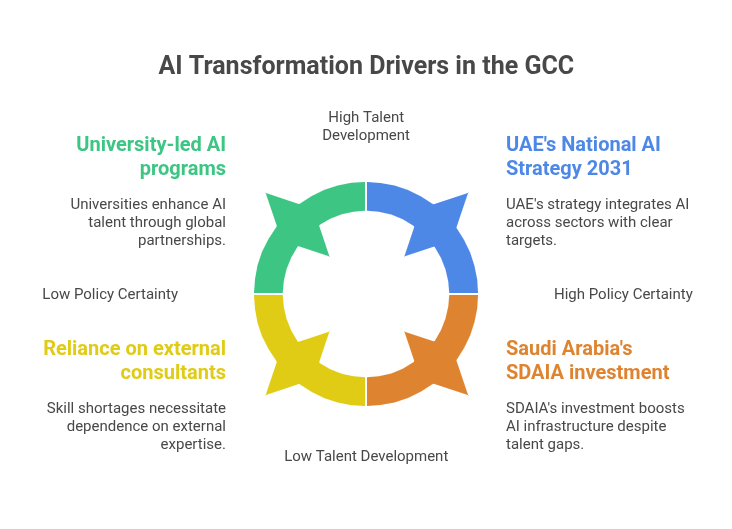
- UAE: The National AI Strategy 2031 will have targets for integrating AI into all government services, education, and the private corporate sector by developing ethical frameworks and sector readiness.
- Saudi Arabia: The Kingdom’s SDAIA has pledged that over 70% of public services will be injected with AI by 2030, sustained by a $20B+ investment blueprint for infrastructure and research.
- Qatar: The National AI Strategy prioritises the integration of AI technologies for healthcare, sport analytics, and smart infrastructure, aligning with its Vision 2030 diversification plan.
Corporate-specific compliance guidelines
- Saudi Central Bank (SAMA): AI usage guidelines for BFSI sectors, focusing on explainability and bias fact mitigation.
- The UAE’s Ministry of Health and Prevention has defined AI standards for healthcare diagnostic systems.
The end result is regulatory confidence, allowing CIOs and CTOs to design AI architectures with clear guardrails, which helps avoid the legal ambiguity that can slow down such projects in other regions.
2. Development of Talent at Speed and Scale
Until now, a shortage of skills in the region has largely limited them, leading to a heavy reliance on external consultants. Envision 2025 for a change.
University-led AI programs
- Khalifa University, KAUST, and Qatar University now have bachelor’s, master’s, and PhD programmes focused on AI.
- Adopting partnerships with MIT, Oxford, and other global institutions brings cutting-edge research to the region.
New government reskilling programs
- The UAE’s “One Million Arab Coders” initiative has now expanded to include AI and machine learning certifications.
- Bootcamp: SDAIA, Saudi Arabia, has launched AI boot camps which target 25,000 trainees each year.
Hybrid delivery models
- Companies are starting to combine local presence experts and partners’ offshore AI engineering teams, such as Esferasoft, which allows for very high-speed delivery while creating internal capacities.
Esferasoft insights: GCC clients that invest in in-house AI literacy training – not just data scientists, but also business analysts, process owners, and compliance officers – achieve faster adoption curves and smoother change management.
3. Infrastructure that Matches Ambition
Ambitions about AI will mean little for the GCC without cloud and connectivity infrastructure to support them. Here, the region moved aggressively:
- Presence of hyperscalers in region
- AWS Middle East (UAE) Region and AWS Middle East (Bahrain) Region
- Microsoft Azure UAE Central & UAE North, besides Azure Saudi Arabia (in partnership with local entities)
- Google Cloud Doha Region
- Oracle Cloud Riyadh Region
These regions fulfil all data residency requirements while also providing low latency for real-time decision-making and AI inference.
Proliferation of 5G
GCC states have been ranked the highest in the world with regard to 5G, essential for edge AI in smart cities, ports, and logistics hubs.
Ecosystems of IoT and sensors
Investments in smart infrastructure like NEOM in Saudi Arabia or Masdar City in the UAE are producing large volumes of sensor data, from which real-time data can be harvested to feed analysis.
4. Sectoral Readiness and Competitive Pressure
Certain sectors are advancing rapidly because of competitive dynamics and clear return on investment (ROI) for their applications.
Certain industries are moving faster due to competitive dynamics and clear use case ROI:
| Sector | Readiness Level | Key AI Adoption Drivers |
| Oil & Gas | Advanced | Predictive maintenance, safety monitoring, energy optimization |
| BFSI | Advanced | Risk analytics, generative AI for customer engagement, fraud detection |
| Public Sector | Scaling | Smart city initiatives, citizen service chatbots, process automation |
| Healthcare | Emerging | Diagnostics, patient flow optimization, telemedicine |
| Retail & Logistics | Emerging | Demand forecasting, personalized offers, last-mile route optimisation |
According to Esferasoft, there is significant peer pressure in the GCC. Once a leading bank, oil company, or government department demonstrates the ROI of AI, competitors respond swiftly to avoid stagnation.
5. Why 2025 Is the Inflection Point
The main difference now between 2025 and even two years before is that the blocks have aligned:
- Defined supplementary safe harbour.
- Local and hybrid talent pipelines exist.
- Sovereign infrastructures are functional.
- Proven cases delivered measurable ROI.
The combination allows companies to migrate from isolated AI experiments into enterprise-wide AI platforms—without encountering the roadblocks that previously impeded progress.
Trend #1 – Generative AI Copilots for Bilingual Workplaces
The Gulf Cooperation Council’s (GCC) business culture is by nature bilingual; presentations in boardrooms may be conducted in English, but government filings, court records, and much of the communication with citizens must be in Arabic. Most organisations conduct each major transaction in both languages.
Middle Eastern businesses are adopting AI for the following reasons:
- When AI systems are limited to only one language, the customer experience will suffer.
- Mistranslation or poor contextual comprehension may also jeopardise regulatory compliance.
- Manual reformatting or retranslation of outputs generated by AI would reduce the productivity of employees.
AI technology through which the leaders of the Middle East deploy:
- Function-tailored copilots: These are specifically designed for bankers or engineers or service agents and are directly connected to ERP and CRM.
- Bilingual NLU models: They are tuned on both Modern Standard Arabic and English corpora and include industry-specific jargon.
- Voice-enabled copilots: They are used in field service environments where hands-free operation is critical, such as oil platforms or remote utilities.
Effect metrics observed for AI Consulting Projects in the Middle East:
- 25% faster turnaround for two-way bilingual contracts for a leading bank in the GCC.
- Translation outsourcing saves close to 60% for a government agency.
- An 18% increase in CSAT for a telecom provider with bilingual self-service portals introduced.
Trend #2—Data Sovereignty and Trusted AI Governance
Data placement and treatment are equally as important as the sophistication of the model for the delivery of artificial intelligence services Middle East. Data sovereignty regulations within the GCC are strict, and the design of any AI-enabled business solutions will have to accommodate those from the outset.
Enterprises in the Middle East demand the following key features of sovereign AI solutions:
- Localised hosting: With the appropriate choice of AWS UAE, Oracle Riyadh, or Azure Saudi to keep data within borders.
- Granular access control: Role-based permissions with just-in-time access for sensitive data.
- Transparent AI decision-making: Allowing decentralised explainability of models and tracing of decision paths to satisfy regulators within BFSI or health sectors.
Esferasoft case:
An insurance company in the Middle East used our policy-as-code framework to ensure that customer health data was never exported from the UAE while still allowing for analytics in the region. The system has successfully passed several third-party compliance audits without requiring any changes.
Why it matters:
Governance earns avoidance of penalties and complements consumer trust, which constitutes a critical differentiator in a highly competitive industry with high stakes.
Trend #3 – Modernisation of AI and ERP, and MLOps
These operational hearts of the many enterprises across the GCC have been around traditionally as historical ledgers rather than engines of prediction.
Consultants in AI in the Middle East advocate for modernisation through:
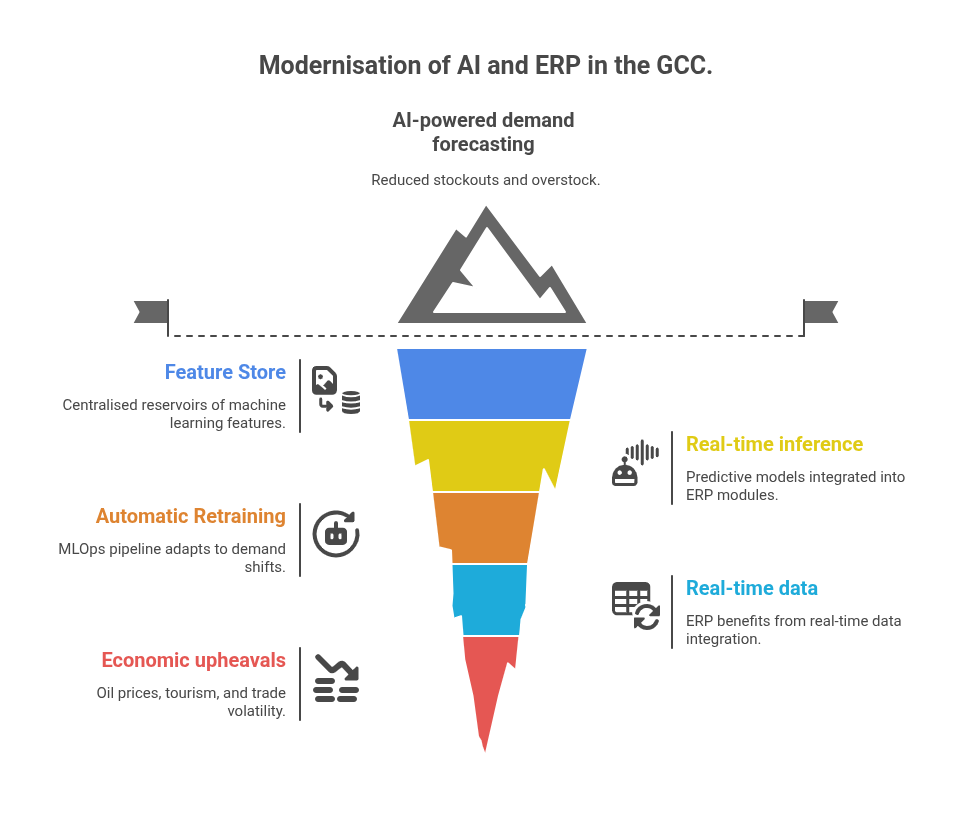
- Feature Store: Centralised Reservoirs of Machine Learning Features Sourced from ERP Transaction Revenue.
- Real-time inference: Predictive models integrated into procurement, sales, or HR modules.
- Automatic Retraining: The MLOps pipeline will automatically change due to seasonal demand shifts or supply chain disruptions.
Examples of Such AI Usage in Middle East Companies:
A retail business in the UAE has put in place AI-powered demand forecasting within its SAP framework, leading to reduced stockouts by 22% and overstock reductions in the first year by 15%.
What is speeding the trend up?
As real-time data should increasingly become an ERP for the benefit of board-level priority, it is becoming an increasingly loud argument given the current upheavals in oil prices, cycles in tourism, and volatility in trade.
Trend #4 – Edge AI, IoT & 5G for Industries and Infrastructures
GCC’s mega projects and heavy industries, along with vast logistics hubs, produce tonnes of data streams from sensors, cameras, and connected devices. Sending all of that to cloud processing inevitably has many inconveniences; hence, the emergence of edge AI solutions that are being ramped up by industry leaders in the Middle East.
Example deployments:
- Ports: Edge-based image recognition for container ID scanning and customs inspection in Jebel Ali and King Abdulaziz Port.
- Smart cities: Real-time pedestrian safety systems in Riyadh’s NEOM development.
- Oil & gas: Pipeline leak detection using an on-device inference to trigger automatic shut-offs.
Business case:
Edge AI brings latency down from seconds to milliseconds, ensures more uptime in the remote areas, and cuts down data transfer costs due to the fact that a majority of the processing is carried out locally.
Trend #5: Cybersecurity Artificial Intelligence powers these solutions.
Cyber risks complement the exciting growth of AI innovation across industries in the Middle East, now including employing AI to enhance phishing campaigns, locate unprotected systems, and automate attempts at intruding.
How AI technology Middle East SOCs are responding:
- Disparate Detection: AI will be able to identify irregularities in both login patterns and transaction flows.
- Threat Intelligence Copilots: Summarising threat feeds, correlating with past incidents, and suggesting relevant actions.
- Automated Playbooks: AI-orchestrated, automated isolation of compromised endpoints within seconds.
To illustrate:
A prominent Gulf bank has reduced its average time to detect security incidents by 45% by integrating Esferasoft’s AI-enhanced detection-as-code modules into its SOC platform.
Trend #6—Intelligent Automation: RPA + Process Mining 2.0
Automation in the GCC is at its second peak, after its first, which employed traditional RPA focusing on task automation. It mimicked human clicking or keystrokes in speeding up repetitive back-office activities. However, traditional RPA could not handle unstructured data, bilingual content, and dynamic workflows needing judgement or context during execution.
Moreover, the invention of intelligent automation advanced by artificial intelligence will be adaptive, insightful, and scalable.
Misleading claims that have failed mainly manifest artificial errors in their use of AI by companies in the Middle East.
Unstructured Data Handling:
AI-powered OCR and NLP extract information from handwritten Arabic or English forms, including invoices and service requests.
For example: Insurance claims recorded in Arabic are immediately put into a digital format, translated and processed without any human intervention.
Voice & Audio Understanding:
- The system transcribes voice calls into text, incorporating sentiment analysis for monitoring compliance violations and customer dissatisfaction.
- The system finds its primary application in BFSI and healthcare sectors, where call quality and handling hold significant importance.
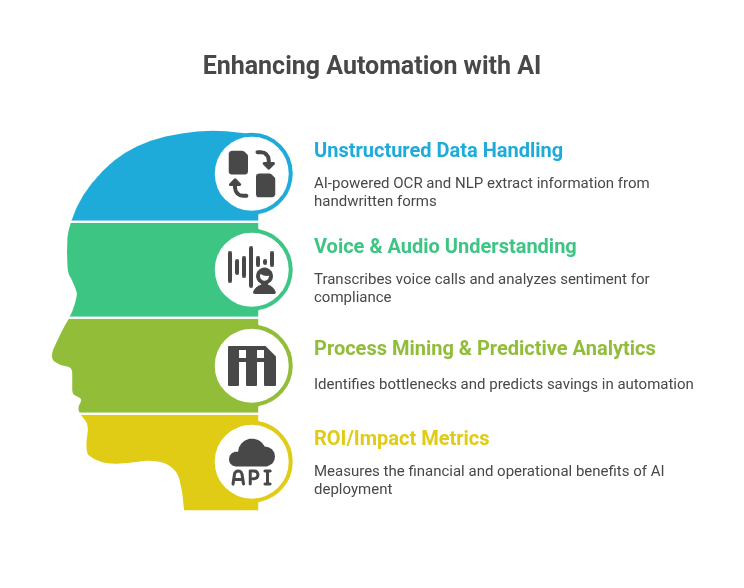
Process Mining + Predictive Analytics:
- Modern tools function against the scanned layout of traditional job execution in an ERP, CRM, or ticketing system to escape from any bottleneck and provide for “what-if” simulations.
- Predictive models are used to estimate the potential time and cost savings even before automation takes place.
- Integration with AI-based business solutions that Middle East enterprises already use
These co-pilots include an AI-based solution, ERP analytics, and predictive maintenance, all of which facilitate end-to-end organisational transformation towards automation.
ROI/Impact Metrics
- Most AI deployments typically return 200% of the first-year Contact pledge.
- 40%—60% time reduction in manual processing.
- 25%-35% reduction in error rates for high-volume processes.
Esferasoft’s AI consulting Middle East suggests combining RPA with process mining and AI insights to make automation work better and faster, while also being more flexible and able to handle changes in the business.
Trend #7 — Digital Twins & Predictive Maintenance
The GCC economy heavily invests in oil and gas, utilities, transportation, and large-scale manufacturing sectors due to their high asset structure. The cost of downtime in these sectors would extend up to millions of dollars daily, and that’s why digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets or systems—are gaining importance as one of the biggest AI solutions for providing value in the Middle East.
Working of AI-based Digital Twin
- Data Integration: The real-time IoT sensor data feeds into a virtual model of the asset.
- AI Simulation: The algorithms of machine learning evaluate historical performance, environment, and other operational variables to predict outcomes.
- Scenario Testing: Operators can perform “what-if” simulations before the alteration of a physical asset.
- Predictive Maintenance Alerts: AI raises anomalies before any breakdown-caused action to conduct its proactive maintenance.
Industry applications for AI innovation in Middle East industries
Oil & Gas:
- Operators of refineries use twin processing units for the evaluation of process optimisations without any risk to live operations.
- Artificial intelligence further simulates corrosion rate predictions under various conditions in pipelines to ensure timely maintenance.
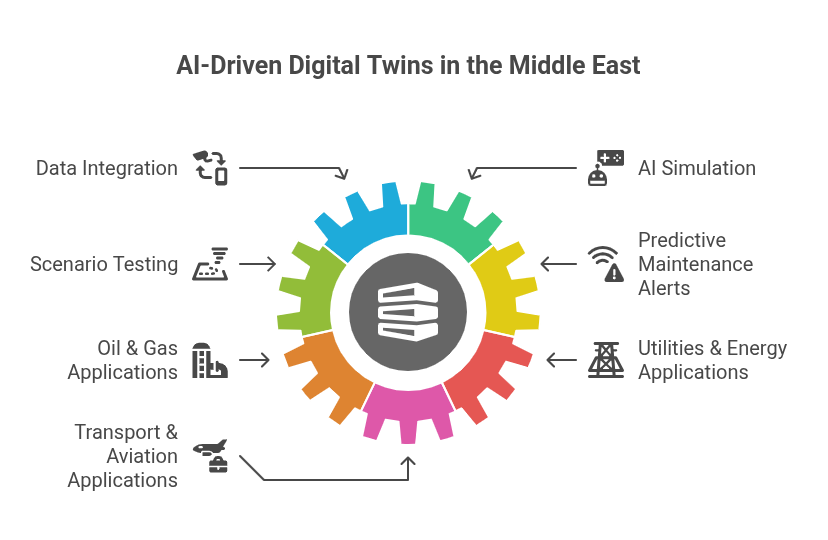
Utilities & Energy:
- Electricity suppliers construct twin power grids to balance loads across transformers and to schedule maintenance effectively.
- Wind turbine twins in renewable energy farms in the UAE predict output and identify losses.
Transport & Aviation:
- Airports create digital twins of passengers to optimise staffing at security checkpoints based on their upload patterns.
- Airlines test patterns of fuel consumption and wear for different flight plans. Proven business outcomes:
- 20-to-25 percent increase in asset life
- 30-to-40 percent less unplanned downtime
- Maintenance cost decreased by 15-to-20 percent
This matters because AI is gradually developing in Middle East businesses.
Maintenance is transformed from a reactive centre to a proactive profit enabler, based on the concept of “digital twins,” which fits quite well with sustainability goals that seek to waste less and maximise the lifespan of assets because a smaller carbon footprint results from manufacturing and replacing parts.
Trend #8 – AI for Sustainability & ESG Reporting
The meaning of sustainability is going to the other side and changing from a marketing differentiator to complying with legal obligations in the Middle East. With initiatives like Saudi Vision 2030, the UAE Net Zero by 2050 strategy, and Qatar National Vision 2030, ESG performance is now directly tied to licensing, eligibility for an investment, and public perception.
AI-powered business solutions Middle East leaders are turning to artificial intelligence services Middle East to make ESG compliance both more accurate and also less burdensome.
The Challenge
Most large enterprises in the region operate across multiple jurisdictions, with complex supply chains and diverse reporting obligations. This creates problems:
- Data silos: Emissions and waste data spread across IoT systems, spreadsheets, and third-party reports.
- Manual processes: ESG reports often require months of manual aggregation, validation, and formatting.
- Risk of greenwashing accusations: Without verifiable and auditable data, claims of sustainability can backfire.
How AI technology is helping Middle East organisations with ESG
Automated Data Collection & Integration
- IoT sensors in manufacturing plants, ports, and logistics hubs collect real-time metrics on energy usage, water consumption, and emissions.
- AI-powered connectors combine these feeds into a cohesive platform for sustainability data.
Data Cleansing & Validation
- A Machine Learning model will be used to identify any anomalies, missing entries, or outliers in ESG data and to ensure the data is correct before reporting.
- AI will reconcile conflicting data sources, i.e., when supplier reports don’t match internal measurements.
Framework Mapping
- AI maps the collected data against ESG standards, e.g., GRI, SASB, TCFD, or region-specific frameworks, such as SASO sustainability guidelines in Saudi Arabia.
- Automatic updates ensure compliance in cases when frameworks change.
Predictive Sustainability Modelling
- This AI predicts the future ESG performance on the basis of historical data, operational changes, and seasonal trends.
- This helps in pre-emptive actions, i.e., rescheduling equipment upgrades to postpone emission peaks.
Bilingual ESG Reporting
For public-sector and government-linked companies, AI generates ESG reports in both Arabic and English, easing stakeholder communication.
Industry examples in adopting AI in Middle East businesses
- Logistics: AI route optimisation by a supply chain operator in the U.A.E. led to a 14% reduction in diesel consumption and, finally, to the automatic generation of ESG impact statements for the company’s annual reports.
- Energy: An AI-based IoT monitoring system implemented by a Saudi utility company led to an 11% reduction in cooling system water usage, which went straight into their sustainability metrics dashboard.
- Retail: AI demand forecasting system implemented by a retail chain in Qatar reduces overproduction waste by 19%, satisfying both cost savings and ecological targets.
Quantifiable business impact of AI solutions Middle East enterprises see in ESG
- The ESG reporting cycle went from 3–4 months to less than 4 weeks.
- Operational efficiency gains translate to 5–12% cost savings on resource consumption.
- Increase the chances of green financing and preferential procurement contracts.
Why it matters now
GCC investors, lenders, and regulators are steadily mandating auditable, data-backed ESG disclosures. AI consultants in the Middle East, like Esferasoft, help firms shift from reactive compliance to proactive sustainability management, which empowers them to:
- Get ESG-linked financing at a more favourable interest rate.
- Become eligible for government-led sustainability procurement programmes.
- Enhance reputation through verifiable performance data.
Liability and Feasibility of AI Implementation in the Middle Eastern Enterprises by 2025
Turning AI trends Middle East 2025 into reality is a Herculean task. Whether in the Middle East or GCC countries, the vast majority of AI pilots can be divided into those funded by multi-year ROIs and those that simply bob along on budget.
This trained Esferasoft delivery within AI services Middle East adopted a balanced approach to the adoption scheme quickly, along with a strong leadership strategy.
Step 1 – Identify Your Business Problem Not First Technology
Start instead with,
- Where are we losing as much time or money?
- Which processes frustrate customers or employees the most?
- What pain points exist within the organisation that AI might help alleviate?
Example: One loss identified by a Saudi retail chain was stockout loss, and AI-driven demand forecasting provided an 18% improvement in inventory turnover within six months.
Step 2 – Build on Sovereign & Compliant Foundations
Given the realities of AI advisory in the Middle East, it is crucial to prioritise data sovereignty and governance in every pilot project. This means:
- Hosting critical workloads in cloud regions based in the UAE, KSA, or Qatar.
- Embedding policy-as-code frameworks for automated compliance checks.
- Using explainable AI models for BFSI, healthcare, and government workloads.
Esferasoft has reduced the approval cycles for projects by up to 40% for a GCC bank that is implementing generative AI copilots as part of its compliance-by-design initiative.
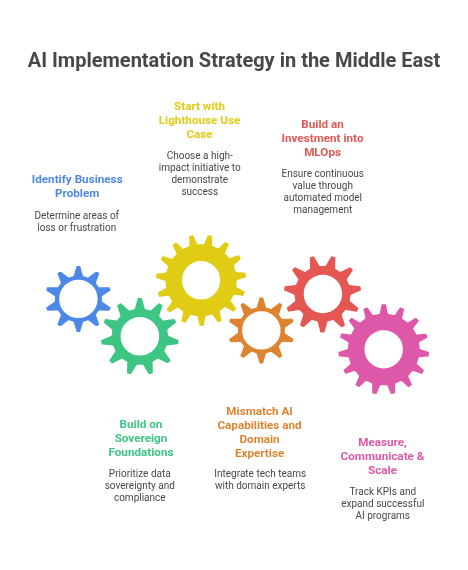
Step 3 – Start with a Lighthouse Use Case
Choose one high-value, high-visibility initiative to demonstrate impact and build internal momentum.
- Bilingual generative AI copilots for call centres
- Predictive maintenance in oil and gas
- Automated ESG reporting for energy companies.
These lighthouse projects:
- Deliver fast ROI.
- Build stakeholder confidence.
- Create reusable AI infrastructure components for the future.
Step 4 – Mismatch AI Capabilities and Domain Expertise
Middle East countries lose when tech teams in businesses function in silos. In contrast:
- Create mixed-functional squads – process owners, data scientists and compliance experts.
- Follow hybrid delivery models – local teams for governance, offshore talent for engineering scale.
- Provide AI literacy training to non-technical leaders.
When all process owners receive basic AI training, Esferasoft has observed a doubling in the pace at which organisations adopt AI.
Step 5 – Building an Investment into MLOps for Continuous Value
Without care, AI models degrade. MLOps ensures:
- Automated retraining when there are changes in the market or environmental conditions.
- Real-time checking for bias, drift, or accuracy drop.
- Faster rollout of model improvements in production.
This is why AI solutions Middle Eastern leaders are embedding MLOps directly in ERP and CRM modernisation programs.
Step 6 – Measure, Communicate & Scale
All AI programmes require:
- Specific KPIs on day one.
- Periodic reporting to leadership with business outcomes rather than technical metrics.
- Governance boards to approve scaling into new domains.
For example, a UAE energy company increased its predictive maintenance AI from 4 turbines to 28 within a year, only after proving a $4.2M annual saving in the pilot.
Esferasoft’s Proven Guide on AI Delivery
After attending multiple engagements with GCC, we found out that we have defined this approach as an emerging repeatable framework:
- Discovery and Prioritisation – Identify process pain points mapped to AI opportunity.
- Governance Design – Compliance, sovereignty, and explainability baked in from day one.
- Prototype into Reality – Sprint within 8 to 12 weeks to deliver functional pilots.
- MLOps and Integration – Glue into existing ERP, CRM, and IoT platforms.
- Scaling and Training – Scale to other units while developing internal capabilities.
Possibility to Powerhouse: The AI Leap in the Middle East by 2025

By then, the approach to AI will be clear, with strong political support, solid infrastructure, and a skilled workforce working together effectively. The eight trends currently shaping AI innovation in Middle East industries are not only futuristic concepts anymore; they are now delivering real-time results in banking, energy, logistics, healthcare, and governance.
From AI tools that help with language to systems that manage regulations and digital replicas that minimise downtime, these AI services Middle East are being effectively used by service providers in the Middle East.
The playbook is clear for businesses:
- Be early: Edge to grab goes into the hands of swift players.
- Focus: Start with high-impact lighthouse projects.
- Stay compliant: Governance and explainability are non-negotiables.
- Grow talent building: Combine technology with in-house expertise.
At Esferasoft, our AI consulting Middle East engagements prove that when strategy meets execution, companies don’t just adopt AI — they lead with it.
In another sense, the Middle East has ceased to be an emerging market concerning AI; it is, instead, growing into one gigantic AI powerhouse. Given the right vision, governance, and partnerships, 2025 is the year where GCC enterprises will set the benchmark for AI-enabled business excellence at the global level.
The future is not coming here; the future is being built here. To learn more, contact us today at +91 772-3000-038!
FAQ’s
1. What are the top trends for AI consulting in the Middle East in 2025?
Copywriting in two languages, sovereign AI governance, MLOps for ERP modernisation, edge AI through IoT and 5G, AI for cybersecurity, intelligent automation, digital twins for predictive maintenance, and ESG reporting enabled by AI.
2. Which industries see the most benefits from AI services adopted in the region?
Banking and finance, oil and gas, government, logistics, utilities, healthcare, and retail show early dominance when it comes to AI adoption in Middle East businesses due to clear ROI and competitive pressure.
3. What role do governments in the Middle East play in promoting AI adoption and consulting?
The government has put in place various national strategies, investments in sovereign cloud infrastructure, reskilling programs, an ethics framework for AI operations, and sector-specific guidelines for compliance as a means of facilitating the adoption of AI consulting.
4. What is the main reason for the rush of Middle Eastern businesses towards AI consulting?
Regulatory clarity, infrastructure readiness, operational efficiency, bilingual business environments, and competitive pressures are driving the need for consulting.
5. What will be the top AI technologies and solutions in demand in 2025?
Generative AI, predictive analytics, computer vision, intelligent automation, MLOps platforms, ESG data platforms, and bespoke AI models are some AI technologies and solutions in demand in 2025.
6. How does AI consulting help in regulatory compliance and data privacy in the Middle East?
This starts from day one with designing solutions to include concepts themselves, such as data sovereignty, policy-as-code frameworks, understandable AI, and other sector-specific compliance requirements.
7. What would the role of local, as well as international, AI consulting companies be in transforming a business endeavour?
Local firms lend culture as well as regulation and language expertise; international players bring state-of-the-art technology capabilities. Many successful projects use both hybrid delivery models.
8. How can businesses look for their ideal consulting partner for AI in the Middle East?
Look for proven GCC project experience, sector expertise, compliance readiness, bilingual AI capabilities, and the ability to deliver both quick wins and scalable platforms.
9. What barriers do organisations in countries in the Middle East face when it comes to AI solutions?
Organisations in the Middle East encounter challenges such as skill shortages, resistance to change management, issues with data quality, complexity in integration, and the need to navigate multi-jurisdictional compliance requirements.
10. What should future trends in AI services prepare Middle East businesses for in the years ahead?
Expect more growth in AI-powered business solutions Middle East, fully autonomous operations in most of the supply chain and logistics, healthcare AI diagnostics at scale, AI-powered trade finance, and regional AI innovation hubs that export.



