|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
AI is becoming increasingly integral to business strategy – from intelligent customer experiences to advanced analytics. However, this has introduced new risks in terms of bias, security vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps, making trust an increasingly tenuous commodity. In this regard, companies need much more than technical advancement but also a proper system of governance.
The AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), introduced in 2023 by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, formalises the structure. Built around the principles of governance, mapping, measurement, and management, it assists organisations in identifying and mitigating risks without slowing down innovation.
At Esferasoft, we are aware that every organisation must strike an appropriate balance between growth and responsibility. NIST AI RMF provides all those ways to ensure AI systems are reliable, trustworthy, and compliant with upcoming regulations. This blog unpacks what the framework is and what business AI risk management must contain.
NIST AI RMF refers to the NIST AI Risk Management Framework.
The comprehensive AI RMF identifies and evaluates risks associated with AI systems; it helps the organisations mitigate these risks. AI RMF is a complete guide from the US National Institute of Standards and Technology, released in January 2023 to allow organisations to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks within the lifecycle of artificial intelligence – from design through development to deployment and monitoring.
It is tailored specifically to the unique challenges of AI, such as bias in datasets, understandable gaps for complex models, and unpredictable outcomes in real-world situations. It also presents obstacles in how one measures outcomes beyond accuracy. This dogma offers a basis on which to solve these questions while pushing favourable innovation along the path.
The framework is organised into four main functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage. Together, they create a cycle of accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement. The RMF presents Profiles, a new concept through which organisations can tailor the framework to their specific sector, risk appetite, and use cases.
NIST AI RMF is one of these minds that actually concerns reason, providing a fine mixture of flexibility with structure. Yet it is also placed in alignment with existing and emerging global standards, such as the EU AI Act and the OECD AI principles. Thus, for enterprises that have a global footprint, it serves as a very practical baseline for AI governance.
Through the AI RMF, organisations will acquire more than just compliance preparedness – they’re able to build systems that are more resilient and trustworthy and aligned more with strategic themes. These positions would allow them to innovate boldly with protection on their reputations, customers, and long-term business value.
Why Enterprises Should Care About AI Risk Management
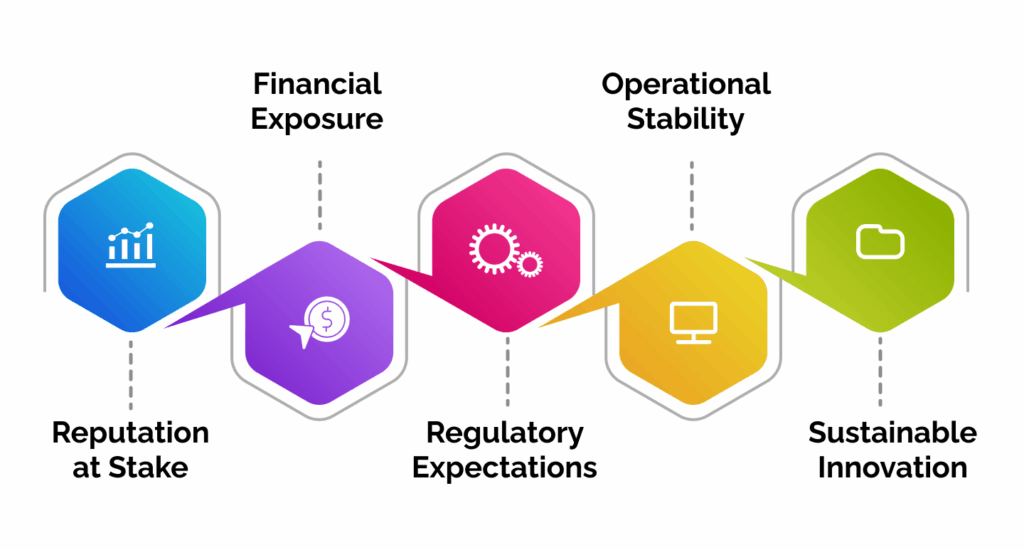
Reputation at Stake
AI systems demonstrating bias or resulting in unfair outcomes can terminate public trust in a matter of moments. A discriminating hiring tool or a medical algorithm misclassifying patients can reverse efforts toward brand building, extending over several years. Enterprises must protect their reputation against untrusted AI, with fairness and transparency being their absolutes.
Financial Exposure
Poor AI decisions incur real-time costs. Moments of direct losses for enterprises may come from mispriced financial products to wrong inventory forecasts. If structured in a risk framework, vulnerabilities could be identified early enough to deliver costly lessons.
Regulatory Expectations
Governments and regulators watch closely to hold enterprises accountable. Frameworks like the EU AI Act and U.S. guidelines demand monitoring. With NIST AI RMF as a guiding standard, organisations are preparing to be compliant even before that becomes the law.
Operational Stability
Untamed AI will disrupt the orderly flow of business or simply expose the systems to become the prey of attackers. Disruption may stem from subordinate risks framed as adversarial intervention, downtime, and misuse of sensitive data, all of which call for a relentless vigilance. Proper management of these risks would help to keep operations sound and resilient.
Sustainable Innovation
Risk management will not slow down AI; it will promote its sustainability. Whichever enterprises can balance speeds and responsibility are the same enterprises that will be able to innovate with confidence and earn the trust of customers, regulators, and investors.
Esferasoft assists enterprises in embracing the NIST AI RMF in order to achieve this balance. When risk is managed, AI becomes much more than a tool for efficiency – it transforms into a trusted vehicle for long-term business success.
The Core Functions of the NIST AI RMF
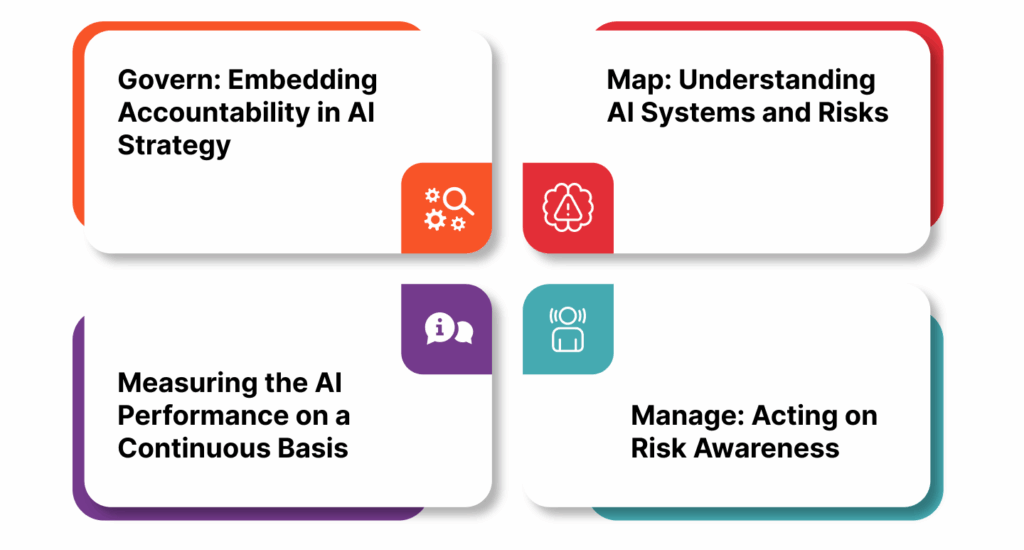
NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework consists of four interrelated functions: govern, map, measure and manage. These four functions together guide enterprises toward the innovative yet responsible, transparent, and resilient design for the AI systems.
1. Govern: Embedding Accountability in AI Strategy
Governance is the key component of AI risk management. It deals with setting policies within the organisation, defining roles, and building an accountable culture around AI. For enterprises, governance ensures that decisions about AI don’t reside solely with tech teams; it becomes an organisation-wide priority.
Some highlights are:
- Formation of some AI ethics boards or high-level steering committees.
- Adopting internal policies aligned with the laws and industrial standards in force.
- Foster interdisciplinary outreach and training for relevant staff on responsible AI use.
Enterprise Examples: A global bank establishes an AI ethics committee that reviews credit risk models to guarantee fairness and regulatory compliance. This prevents unintended discrimination while augmenting the trust of customers and regulators.
2. Map: Understanding AI Systems and Risks
Mapping is the clarity and context thing for organisations to say what AI systems are intended for, who they affect and from where risks can come in. That avoids “black box” adoption: put AI to work and then ask what its implications are.
Key points include:
- Define system purposes and limitations.
- Reveal under-and-over stakeholders, whoever they are.
- Prepare for surprises.
Enterprise Example: An international bank formed an AI ethics committee to review credit risk models for fairness and regulation. Indeed, ahead of time, they are thus setting up safeguards before actually putting it in gear.
3. Measuring the AI Performance on a Continuous Basis
An AI system can’t simply be developed and left. The Measure function is about a continuous evaluation of the system by using both the technical metric and the qualitative metric. The enterprise must constantly monitor the important issues of accuracy, robustness, fairness, and explainability during the lifecycle of an AI system.
Key aspects include:
- Fairness audits, bias detection tools, and robustness testing.
- Explainability techniques for high-stakes systems.
- Continuous monitoring – paramount in itself – must not be treated merely as a verification approach.
Enterprise Example: A logistics company periodically measures its demand forecasting tool based on AI to ensure it adapts well to seasonal change and does not introduce any bias that may disrupt supply chain operations.
4. Manage: Acting on Risk Awareness
Identifying risks is not enough – everything is based on taking action. The very essence of the word Manage deals with the mitigation, responding to incidents, and changing systems as conditions evolve. It acts to bring down AI risks from theory into addressing them on a proactive basis.
Some Key Elements Are:
- Playbooks – accounting for machine learning model default behaviours – are an essential part of human-devised systems marked by uncertainties.
- Setting modes of rollback and halting operations.
- Adapting to changes in regulations, priority business needs, or performance feedback based on the system.
Enterprise Example: An autonomous vehicle company implements a rapid rollback mechanism that halts any suspect navigation algorithms and reverts to a stable version whenever anomalies are detected on the road.
Profiles: Customise RMF according to Business Needs.
Risks are not the same for every enterprise. This is the reason why NIST introduced Profiles, which can effectively be understood as adaptable templates that would help organisations prioritise functions according to their industry and use cases.
Example of an enterprise:
- A hospital profile emphasises patient safety, explainability, and data privacy.
- An e-commerce profile emphasises transparency in personalisation and resilience in operations.
- Profiles make the framework flexible rather than rigid and therefore ensure an added value across industries.
Importance of the Four Functions Together
The power of functions is executed in the RMF in how they interact with one another; governance sets the tone, context is mapped, insights are drawn from measurement, and action is driven by management. Together, they create the feedback loop keeping AI systems in alignment with business goals, customer trust, and regulatory expectations.
We take enterprises through this cycle – helping them embed the NIST AI RMF in their workflows without slowing down innovation. By embedding these functions, an organisation builds AI systems that are cutting edge but also ethical, compliant, and trusted.
What NIST AI RMF Cohesively Aligns with the Global AI Governance Trends
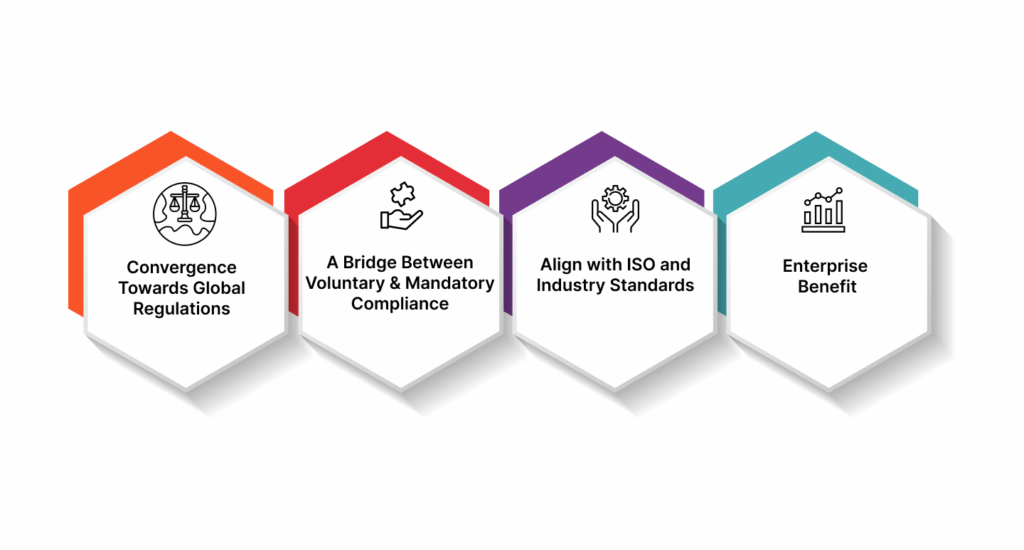
Convergence Towards Global Regulations
AI governance is certainly not a single US issue; there are regulators all over the world trying to set standards. The EU AI Act stakes out a risk-based classification; the OECD principles prefer fair and transparent actions with more personal accountability. The NIST AI RMF supplementarily gives a flexible framework that enterprises can globally adopt.
A Bridge Between Voluntary and Mandatory Compliance
The NIST AI RMF principles are voluntary, unlike the EU AI Act. These principles prepare the enterprises for compliance with stricter regulations. An organisation that follows the RMF practices now will find it easier to adapt to binding regulations in the future.
Align with ISO and Industry Standards
The NIST AI RMF has also been built in line with international standards like ISO/IEC 42001 (AI Management System Standard). This ensures that organisations would be able to easily integrate AI risk practices into existing governance and security frameworks without duplication of effort.
Enterprise Benefit
Global enterprises can take RMF as a standard baseline which can achieve regional harmonisation and lower the complexity of compliance while showing proactive commitment towards responsible AI, a competitive differentiator in heavily regulated industries.
We help companies tailor their use of the NIST AI RMF to suit local and international concerns, ensuring that their AI systems are indeed scalable, compliant, and trusted on a global basis.
Practical Advantage to Enterprises

Trust and Transparency Onto Stronger
Companies can build trust with their customers, the regulatory bodies, and potential partners through the NIST AI RMF’s uptake. Transparency in AI practices reduces scepticism and positions the business in the lane of leaders in responsible innovation.
Regulate Readiness
As regulatory laws on AI come up fast in all nations, enterprises should be wise and avoid future claims on compliance. The RMF serves as the basis that has structured compliance and lessened the risk of fines, penalties, or operational restrictions because of noncompliance.
Operational Resilience
AI systems with continuous oversight and assessment are least likely to fail unexpectedly. The application of the RMF by enterprises means the maintenance of system stability, proactive risk management, and avoidance of costly downtimes.
Reputation and Brand Value
Responsible AI is increasingly becoming a key differentiator. An organisation that embraces frameworks like RMF stands for the adoption of ethics and accountability in its operations and enhances its brand reputation among priority markets.
Faster, Safer Innovation
Risk management does not slow down development; rather, it gives a clear boundary within which experimentation can take place. Therefore, teams of innovation can work with their minds clear, knowing that, regarding the assumptions of safety, fairness, and compliance, the systems are up to par.
Implementation Challenges and Suggestions for their Resolution
Limited In-House Expertise
Very few organisations have teams with the technical and ethical knowledge to apply the AI RMF effectively. If not properly trained, the risk management culture will remain superficial.
Mixed teams consisting of people familiar with data science, compliance, and business should begin forming. Staff should receive ongoing training updates on AI governance.
Legacy Systems Integration
Old infrastructure is often relied on in organisations, which do not easily integrate with modern frameworks. This can create a situation in the embedding of monitoring tools or practices of governance.
Solution: Start with pilot projects, gradually extending RMF principles across systems, with an emphasis on high-impact use cases to demonstrate value before scaling and achieving buy-in from the executive level.
Measuring Abstract Risks
Fairness, transparency, and explainability are concepts difficult to quantify and thus difficult to measure consistently.
Solution: Standardised toolkits and frameworks to evaluate test bias, robustness, and any measure of explainability. Combine mechanised checks with human oversight for balanced treatment.
Concern with Speed versus Responsibility
The urgency to release an AI product commonly contradicts the extended risk assessment.
Solution: Develop pipelines for risk evaluation during implementation. That will promote the ‘safety by design’ environment instead of retrofitting checks for risks.
The above challenges would enable organisations to move from theory into practice, ensuring that the NIST AI RMF really becomes an enabler of innovation, without barriers.
Responsible AI, Real Business Value
Now, AI is ransacking the industries, and by some real risks, it leaves the other side open to investigation. NIST AI RMF provisionally brings the ability of assessment, mediation, and management to organisations to facilitate balancing innovation and accountability—governing AI-related actions responsibly, charting risks before they become disastrous, continuously estimating system functionality, and managing the optimum outcome.
For organisations, application toward AI RMF would mean more than just being ready for compliance; it involves building systems that customers trust, regulators respect, and other stakeholders value. Organisations that infuse this framework allow themselves to be one of the few to prosper as regulators shift the playing field towards responsible innovation.
At Esferasoft, we help enterprises walk the bridge between their AI ambition and AI responsibility. Our knowledge in enterprise AI implementation ensures that risk management is never an afterthought but rather a major contributor to sustainable growth. To know more, call now at +91 772-3000-038!