|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
AI has revolutionised business operations by enabling intelligent systems to autonomously make dynamic decisions, reason, and act independently. Central to these intelligent systems is the agent architecture – the intelligent agent structure framework that defines how an AI agent perceives the world, how it processes perceptions for taking decisions, and how it performs actions effectively.
An AI agent architecture, well designed, forms a modular and scalable basis on which new technology can easily integrate, transitioning from one to another, in addition to alleviating the complexity of advanced AI systems. By providing a clear definition of the common touch points of the core components (typically perception, reasoning, memory, planning, and action), businesses can build a strong foundation for scaling their AI systems, thus also improving maintainability and future-proofing their demands.
Whether you are a developer crafting exceptional AI solutions, a CTO managing digital transformation, or an AI team leader promoting innovation, understanding the principles of AI agent architecture is essential. This guide will walk you through key concepts, practical design patterns, and strategic considerations related to creating great, future-proof AI systems that are specifically aligned with your organisation’s needs.
Need tailored guidance or a customised AI agent architecture solution? [Talk to our team].
Core Components of AI Agent Architecture
An efficient architecture of AI agents requires smooth interactions among several critical components. Let’s put them clearly:
Perception Module
The perception module acts as the sensory organ for the AI agent, collecting and interpreting environmental inputs via sensors, APIs, or user inputs. It is designed to transform raw data into an organised, processed format for future actions.
Reasoning Engine
The reasoning engine involves applying logical algorithms and machine-learning models to make rational decisions. It then combines both acquired and new knowledge to formulate strategic actions, thus enabling the agent to adjust itself dynamically to its environments.
Memory / Knowledge Base
Storing context and history is paramount. A good knowledge base gives the AI agent the context to refer to past interactions and domain-affiliated information for more accurate choices.
Planning and Goal Management
AI agents need clear goals. Prioritise the module in terms of predefined or dynamic changes to such goals. It thus enables intelligent performance of tasks and resources management for optimal use.
Action Module
The action module performs the reasoning engine’s output decisions. It translates the output into interaction with the environment or interacts with people through physical or digital outputs, thus closing the loop of the agent’s interaction cycle.
Communication Layer
This is primarily in an AI multi-agent architecture setting. The communication layer promotes interaction between agents themselves or with human users. This feature makes sure that there is real-time cooperation and harmony in operation.
Looking for expert guidance to help intelligent agents structure these components efficiently? [Talk to our team].
Types of AI Agent Architectures
Depending on the specific use cases, complexities of environments, and business objectives, it is vital to select the best agent architecture for the given use case. Here are several standard types:
Reactive Architecture
Reactive architectures that focus on real-time responses and direct mapping from perceptions to actions should require extensive processing. Systems that require instant and reliable feedback, like autonomous driving or robotics, serve as an example of such an architecture.
Deliberative Architecture
This architecture allows agents to react beforehand and plan for future states based on what they see at the present moment. This approach involves tough but, nevertheless, important decision-making aspects such as logistics management or long-term strategic planning.
Hybrid Architecture
Mixing the two best reactions along with planning, hybrid architectures balance real-time responsiveness and programmable actions. These architectures are very useful in diverse and unpredictable environments.
Layered Agent Architecture
This architecture divides the functionalities into layers, enabling the organised processing and management of complex tasks. The layers can evolve from each other, making the architecture scalable and adaptable.
BDI Model (Belief-Desire-Intention)
This is the most popular cognitive architecture where agents can imitate human reasoning mechanisms. As a result, agents maintain internal beliefs, desires, and intentions that facilitate an agent to act more intelligently in decision-making, making it useful for conversational AI and complex simulations.
Need help choosing the right architecture for your use case? [Talk to our team].
Architectural Patterns
Effective architectures frequently take certain AI agent system design patterns to ensure flexibility, modularity, and scalability.
Event-driven Architecture
Event-driven designs respond to events instead of polling for updates. This saves on resource consumption and promotes real-time responsiveness.
Microservices-based Agent Deployment
Microservices-based agent deployment provides excellent scaling, fault isolation, and ease of management. The agent services operate independently so that any updates and maintenance can be done in an agile manner without affecting the overall stability of the system.
Modular Architecture
A modular architecture builds AI agent system design components as distinct and replaceable units, enabling simple upgrades and modifications without requiring a major overhaul to the entire system.
Considering architectural patterns but unsure where to start? [Talk to our team].
Multi-Agent System (MAS) Architecture
An AI multi-agent architecture system consists of multiple interacting intelligent agents that often require complex coordination strategies to maintain consistency and pursue common goals.
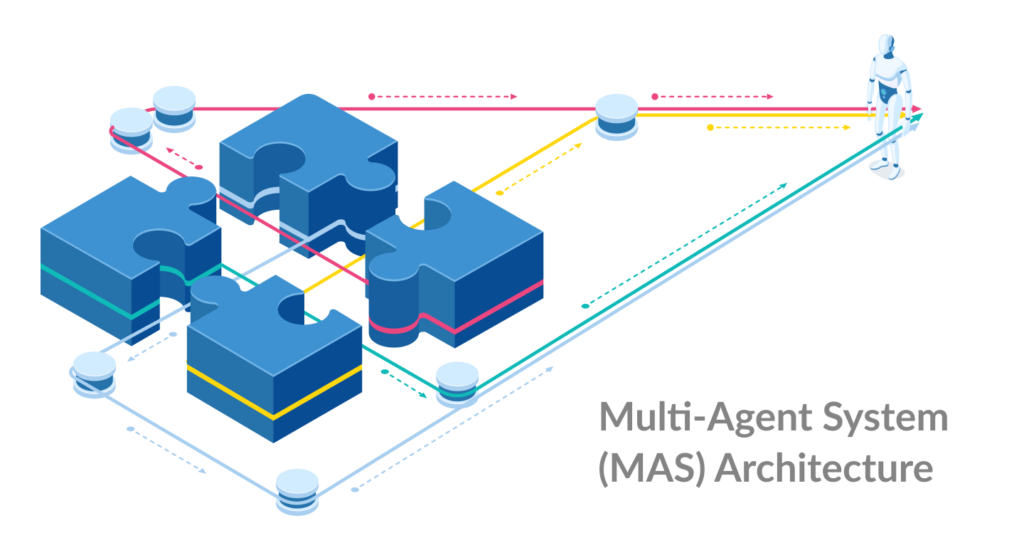
Coordination Mechanisms
The coordination of agents takes place through negotiations, delegations, or centralised mechanisms, which enable them to act harmoniously without engaging in actions that might conflict.
Shared Environment and Communication
It is necessary to have some common environmental context for the MAS. The communications apparatus enables real-time information exchange and decision synchronisation.
Middleware Tools
Tools like JADE (Java Agent DEvelopment Framework), ROS (Robot Operating System), and LangChain ease the development of MAS by providing standard communication protocols, agent management, and lifecycle orchestration.
Need advanced multi-agent solutions? [Talk to our team].
Integration with LLMs & Tools
AI agents are often designed with the capability to work with many types of tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) to increase productivity.
Connecting to LLMs
GPT-4, Claude, and Google’s Gemini are powerful models that provide AI agents with an advantage in natural language comprehension and decision-making, thereby enhancing their intelligence interaction and capabilities.
Using Tools by Plugins and APIs
Most agents are dependent on third-party APIs or use plugins or vector databases for special tasks, such as fetching real-time data, performing complex searches, or even running operations in a domain-specific manner.
The Orchestration Layer
Designed to manage fairly complex but engaging integration tasks, orchestrators such as LangChain or Auto-GPT are used to coordinate gorgeously between LLMs and databases and all sorts of tools, truly simplifying some of the most challenging workflows in AI.
Looking to integrate cutting-edge LLM solutions? [Talk to our team].
Security & Governance Layers
AI agents must be built with security and compliance in mind.
Access Control
Strict access controls guarantee that only authorised personnel or systems will interact with sensitive components or data in the AI system.
Logging & Auditing
Logging and auditing in a comprehensive manner provide clarity for tracing actions and, in turn, compliance with and diagnosis of issues.
Privacy Compliance of Data
Compliance with large-scale standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, and even those for specific regions, is vital. Implementing “privacy by design” protects sensitive information, as it brings it into compliance with the standards.
Want to ensure your AI agent meets rigorous security standards? [Talk to our team].
Deployment Infrastructure
Infrastructure deployment plays a key role in performance and scale in AI applications.
On-Premise vs. Cloud Deployment
While on-premise setups provide better control and security over data, scalability and elasticity are provided by cloud deployment, which are necessary for sensitive or regulated environments.
GPU/TPU Support
Most AI workloads need GPUs or TPUs for optimal operation. It should be mentioned that selection of the appropriate hardware is a critical factor in the overall performance, latency, and cost efficiency of the application.
Edge vs. Central Processing
Latency, connectivity, and resource constraints are the influences that decide between edge and central processing. Edge computing serves real-time applications best, while central processing can perform massive computations due to its greater resource availability.
Need strategic deployment infrastructure planning? [Talk to our team].
Example Architectural Diagram
Below is a clear textual representation of a typical AI agent architecture. This diagram illustrates the systematic flow of information and highlights the modular interaction between various components:
Explanation:
- Communication Layer manages interactions internally between agents and externally with users or systems.
- Perception Module gathers input data from the environment and external sources.
- Reasoning Engine interprets and analyses information, making informed decisions based on models.
- Memory/Knowledge Base stores essential context, aiding accurate decision-making and planning.
- Planning & Goal Management defines tasks and objectives, prioritising them effectively.
- Action Module executes tasks, interacting directly with users, systems, or environments.
- Security & Governance ensures compliance, auditability, and access controls.
- Orchestration Layer integrates the entire system with external LLMs, APIs, and databases, enhancing functionality and capabilities.
This modular, flexible AI agent system design ensures scalability, maintainability, and adaptability, which are essential for robust AI deployments.
Need a detailed, customised visual diagram for your system? [Talk to our team].
Why Choose Esferasoft for Your AI Agent Architecture?
At Esferasoft Solutions, every business is unique and necessitates custom solutions according to the technological, operational, and strategic objectives associated specifically with that undertaking. As such, our approach in designing and deploying AI agent architectures takes a highly collaborative focus toward your business’s requirements.
Tailored and Scalable AI Solutions
Our dedicated team of engineers, architects, and strategists provides AI agent solutions that are perfectly suited to your business’s growth because they are customised for all AI technologies and architectures. Our architectural designs ensure modularity, flexibility, and easy integration, allowing your organisation to quickly adapt to changing business landscapes.
Profound Expertise across Industry Domains
Irrespective of whether the organisation deals with healthcare-related processes, finance, e-commerce, or logistics, Esferasoft has in-depth niche knowledge that makes us more intelligent at contextualising and customising AI agents to notice and respond to outright industry issues.
From A to Z
We take care of all your AI agent needs – from consulting and architectural design down to deploying high-end tools like LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini, Claude) and vector databases and advanced orchestration platforms like LangChain and Auto-GPT. Esferasoft provides smooth deployments, exhaustive testing, and continuous optimisation.
Strong Security and Compliance
At Esferasoft, security is paramount along with privacy and compliance. All AI solutions are completely aligned with international norms like GDPR, HIPAA, etc. Strong governance, logging, auditing, and access-controlling mechanisms have been embedded into the architecture.
Ready to leverage Esferasoft’s expertise for your AI agent architecture? [Talk to our team].
The Importance and Future of Modular, Scalable AI Agent Architectures
The process of building a capable AI agent system starts with intelligent architecture. A well-conceived architecture for an AI agent should do more than provide the requirements of today’s operation; it should create a resilient environment in which long-term growth and adaptability will flourish. The organisations that develop schematically clear, modular, and scalable architectures for AI are the ones best able to capture the benefits of new technological innovations, quickly adopt new capabilities, and remain compliant with regulatory requirements.
Architectural clarity becomes increasingly important because of the increasing complexity of the AI systems consisting of multiple, interacting agents and the adoption of more advanced tools. Focusing on modularity ensures that systems provide flexibility, agility, and simple maintenance, which are necessary for global competitiveness and responsiveness to changes in the technology landscape.
Moreover, the futuristic AI agent architecture may increasingly incorporate additional cognitive capabilities and decision-making abilities. There will be a greater reliance on multi-agent systems and more emphasis on security, compliance, and ethical considerations. Investing now in architectural clarity and robustness is advisable; it is essential.
Ready to create a future-ready AI agent architecture tailored specifically to your organisational goals and technical environment? [Talk to our team today at +91 772-3000-038].