Emergence of AR in Contemporary Engagement
From yesterday’s futuristic stuff to today’s powerful engagement tools in marketing, education, gaming, and e-commerce, augmented reality (AR) transforms its screens into interactive places where users not only view things but also experience them. While shopping avoiding queues and fitting rooms, or a student learning with immersive visuals, AR development dabbled in the mix makes digital experiences dynamic and memorable.
What is AR entail?
The common ingredient that combines all these experiences into one is interactive AR. It brings together the 3D images with motion tracking and real-time response in bringing the digital element on top of the physical reality. The accomplishment deals with gesture, touch or voice; thus, it helps create personalized and immersive experiences. From WebAR product demos to AI-infused training modules, it connects fantasy and reality.
What Will Companies Gain From It
For brands and educators, interactivity through augmented reality can make the experience much deeper, improve retention, and forge stronger connections. It changes curiosity into conversion, turns information into experience, and helps businesses engage, educate, and sell more effectively.
Esferasoft helps businesses design impactful interactive AR VR Development experiences that inspire action. Some of the ways through which our AR content creation services can manifest your ideas in a fresh way with innovation and perfection are:
What Is Interactive AR Content?
Definition and Key Features
Interactive AR content is a type of augmented reality that responds according to the user input, thus sketching a two-way experience instead of a one-way one. It combines both worlds—the physical and digital—through real-time engagement, allowing users to move, touch, speak, or gesture to virtually interact with objects. This may include rotating a 3D model, scanning a product to unveil information, or looking into a virtual scene via a smartphone camera.
Among making it interactive are spatial mapping, gesture control, and AI-driven responses. People do not just view AR—they control it. For this technology, sensors, cameras, and AR SDKs like ARKit, ARCore, and Vuforia learn to track movement and space, thus ensuring a very smooth and natural feel for any interaction.
Different Types of AR Interaction
- WebAR experiences that run directly in a browser without requiring apps.
- AR filters for social platforms that react to facial movement.
- AR applications are used to visualize products wherein users customize or view items in 3D.
- Training simulations that lead users through task-based processes.
Interactive AR is not so much about flashes in the skies as immersion, response, and involvement.
Passive versus Interactive AR
Passive AR uses static overlays, such as scanning a QR code to see an image or looking at a fixed 3D object. The user accepts this but has no part in influencing or determining the experience.
Interactive AR invites comparison. It responds to user actions—rotating, zooming, walking around, or playing with digital objects. The more the system responds, the more advanced the sense of presence felt and the connection made.
This difference is what shifts AR from a novelty into a substantive means of engagement: turning audiences into participants and brands into experiences.

Benefits of Interactive AR Content
Increased User Engagement and Retention
With Interactive AR, users are drawn because they can actively participate instead of just observing. Such increased engagement time comes along with the amount of movement, touching, and exploration involved in the interaction with digital objects. A sense of control will even make the experience unforgettable and keep audiences coming back—whether for fun, knowledge, or retail therapy.
Enhanced Learning and Training Experiences
AR replaces textbook learning with real hands-on, immersive education, where students can explore 3D anatomy, engineers can learn to maintain machinery, and employees undertake safety training in a simulated environment. Interactive AR enables students to experience learning in ways far superior to static materials in both comprehension and memory retention.
Boosted Sales and Conversion for Retail & E-Commerce
For companies, AR bridges imagination with reality. Furniture can be visualized inside the home; accessories can be virtually tried on; products can be previewed before purchase. These experiences cumulatively reduce doubt, build trust, and ultimately create value for incremental conversion rates.
Advanced Brand Recall and Storytelling
AR enlivens a brand story. Instead of mere advertising, companies will create wonderful experiences that consumers can recall—the experience of scanning a product to play a mini-game or viewing an animated story on package graphics. Deeper and longer-lasting emotional impressions are created, boosting recall on brands.
Data Collection and Insights in Analytics
Every interaction of users with the systems generates meaningful behavioral data regarding time in engagement, features browsed, and products viewed. Thus, these insights help brands enhance their content strategies, customize the user experience, and build data-driven marketing decisions.
Interactive AR is far removed from the age of a trend in technology; it is a proven performance-measuring engagement tool that combines creativity, analytics, and customer psychologies.
Applications of Interactive Augmented Reality Content
Retail and E-Commerce
Interactive AR in retail turns shopping into an experience. Customers can now try virtual apparel, see how furniture looks in their own home, or even view 3-D product models from every viewing angle—all in real time. Brands such as IKEA and Sephora have proven how virtual try-ons and AR-based visualizations lower return rates and ultimately reassure customer confidence. Thus, with e-commerce entities, AR adds a special touch of interactivity, keeping users occupied longer and supporting faster purchasing decisions.
Education and Training
AR makes complex concepts alive, visual, and participatory. Learners could explore a 3D solar system, dissect a virtual frog, or learn chemistry through interactive reactions. In the corporate sphere, AR-based training programs allow employees to conduct practice-related tasks in a safe environment—enhancing skill retention while cutting down on on-site training expenses. Technology-based blended immersive-learning opportunities.
Gaming and Entertainment
Gaming has remained the most intriguing arena of possibilities for the use of AR. Examples such as the Pokémon GO game and AR-based interactive storytelling applications suggest that merging the real with the imaginary creates unique immersion. In entertainment, AR filters, interactive ads, and gamified content engage ways impossible for traditional media-forging audiences into participants.
Events and exhibitions
Be it a trade fair or a concert, augmented reality overlays a physical space with some interactive facets. Attendees can scan a banner or booth to gain access to hidden content, participate in an online scavenger hunt, and view holographic demonstrations of a product. That captures audiences well and increases the visibility of brands and participation in the event.
Real Estate & Architecture
Augmented reality allows potential buyers to overcome one of the prime hurdles to purchasing property; consumers can “walk” into spaces before they have been built. Interactive augmented reality walk-throughs and 3D models invite clients to consider various layouts, materials, and lighting options from anywhere. Architects and developers leverage these tools to communicate concepts with dynamism and less revision, thus enhancing clients’ trust.
It is interactive AR’s flexibility that makes it a constant across industries where creativity and functionality meet with the user experience.
Creating Interactive AR Content
Making interactive augmented reality content is a combination of creative design, 3D modeling, programming and testing. It takes many disciplines that can integrate visual storytelling with the most cutting-edge technology to offer believable, seamless, and instinctive experiences.
3D Modeling & Animation
In fact, every single augmented reality experience starts with 3D modeling. Designers use software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max to make virtual objects, environments, and live actors; these models are textured, rigged, and animated so that they can act as intuitively as possible in an augmented reality environment. Realism is the aim—surface reflections, shadows, and physics have to correspond to the real user environment in order to keep at least one immersive aspect.
AR Platforms & SDKs (ARKit, ARCore, Vuforia)
The underpinning for the used technology arises from AR software development kits (SDKs), including ARKit (Apple), ARCore (Google), and Vuforia. They include real-time motion tracking, environment mapping, and object recognition. Precisely thus, they facilitate excellent interactions of AR contents with defined physical spaces—realities—where the digital parts in the realm appear firmly attached.
User Interaction & Gesture Controls
Here is where AR really gets intriguing. This feature is added by developers through gesture recognition, voice commands, and touch enablement to enable users to manipulate these digital objects. For example, by rotating a 3D model or waving one’s hand to animate, or speaking to converse with an AI avatar: Intuitiveness and engagement make up this aspect of AR experiences.
Integration with Mobile Apps or WebAR
After this, using the mobile application or the WebAR system involves including the interactive AR objects. WebAR is mainly useful because users can access 3D representations right through a browser without downloading anything. The format is most suitable for marketing campaigns and product launches, besides education modules that have larger audiences, because it would be easy to possibly reach all who would want to view the project.
Device Testing and Optimization
Culmination in cross-device testing and optimization-to be sure of seamless performance irrespective of whether the AR content is viewed on smartphones, tablets, or AR headsets, each with different processing capability-involves the last phase development. These specifications for optimized augmented reality are enhanced content with illumination, smaller file sizes, and a gentle frame-rate transition for Apple and Android devices alike.
When done right, interactive AR content feels effortless-an invisible bridge between technology and imagination.
Esferasoft AR experts combine art and engineering to create responsive and high-performance AR content tailored to your requirements. From concept to deployment, we create engaging experiences that inspire action and captivate attention.
Tools and Technology Stack
The creation of powerful interactive AR content involves advanced design tools combined with development engines and analytics platforms that play a key role in turning creative ideas into immersive experiences in real-time, indeed engaging the users across devices.
3D Technology Software Blender Maya 3ds Max
Every AR project starts with 3D modeling. This consists of using tools like Blender, Autodesk Maya, or 3ds Max to design, texture, and animate a digital asset that looks true to life. Such models comprise the interactive parts-products, the characters, or environments-explored by users in AR. The mobile optimized assets guarantee smooth rendering and a fast load time.
AR Engines (Unity, Unreal Engine)
These are the game engines that allow AR environments to be created: real-time rendering, physics simulation, and lighting. The above principles are enough to enable real integration of the visuals, animations, and interaction into a consistent experience. Unity has become a popular option for mobile AR, whereas Unreal shines in high visual fidelity targeting enterprise- or entertainment-grade projects.
AR SDKs (ARKit, ARCore, Vuforia)
Introduction of these software development kits as the backbone of any interactive AR system. This technology (spatial tracking, plane detection, and environmental mapping) creates an AR world on mobile through ARKit and ARCore. Vuforia takes object recognition and image-based tracking further and would greatly benefit product visualization or training simulation.
AI Incorporation on Customized & Automated
This was enhanced by artificial intelligence, wherein personalized and automated AR experiences intensified. AI can adapt visuals or scenarios based on user behavior: changing the environment, suggesting products, or creating dynamic dialogue. It can also make AR interfaces more intuitive and accessible through gesture recognition, object detection, and real-time translation.
Analytics Tools to Measure Engagement
These provide information on usage and engagement metrics, including time spent, number of interactions, and conversion rates post-launch. The intelligence gleaned from such analytics can be applied to AR campaign refinements and content strategies. Integrated tools or open third-party platforms like Google Analytics for AR, Unity Analytics, or custom data dashboards will help businesses understand what captivates users the most.
We, at Esferasoft, bring creativity and technology together through our development process that works through these tools to maintain AR content functioning well on all platforms and devices.
Interactive AR Content Powered by AI
AI is reshaping design, delivery, and optimization of augmented reality experiences. Static is turned into a smart, adaptive environment responsive to any particular user. Thus, this opened the door for a variety of new personalizations in informative content, as well as new immersively personal experiences in augmented reality.
AR Adaptation According to User Behavior
With the establishment of AR systems through AI learning, user behavior can determine what they look at, how they move, and which input they interact with. This will help shape the dynamics of the AR experience adaptability. For example, a retail AR app powered by AI can give a customer recommendations for buying other products, while an AR module in education can adapt to the applicable level of difficulty according to the learner’s pace. This type of personalization turns engagement levels up while improving retention.
AI for Real-Time Content Generation
Content in the AR-world need no longer be fully prepared beforehand. Generative AI tools build 3D assets, have backgrounds, or create animations when needed through text-to-speech commands. This takes production time to an entirely different realm while granting scalability and more straightforward customization. Runway, Kaedim, and OpenAI’s Shape-E are some of the few platforms pioneering real-time asset generation for brands for a continuously evolving content journey.
Predictive Analytics for Improved Engagement Optimization
Contrary to their predecessors, AI-powered analytics do not only give a description of what happens, but they also predict future usage patterns in relation to said trends. By studying the interaction data, predictive models determine which features of the experience are most likely to be eye-catchers and at what point users will disengage. Businesses can bring such findings from this model back to refining the AR experience for optimum performance and conversion rate.
Pros and cons of AI in AR
Advantages:
- Heavy personalization and high adaptability.
- Accelerated product cycles through automated asset creation.
- Enhanced analytics for better real-time optimization.
- Greater scaling across industries.
Disadvantages:
- Needs Huge Data Sets for Accurate Personalization.
- High upfront cost in setting up AI integration.
- Complex dynamics in keeping responses natural and realistic.
Nonetheless, these challenges are quickly vanishing as more people gain access to AI. The combination of AI and AR heralds a change from interactive content to intelligent experiences—each interaction feels uniquely crafted.
At Esferasoft, we adopt engaging solutions that involve AI-enabled AR whereby businesses will personalize, predict, and perform powers to create experience evolutions alongside their users.
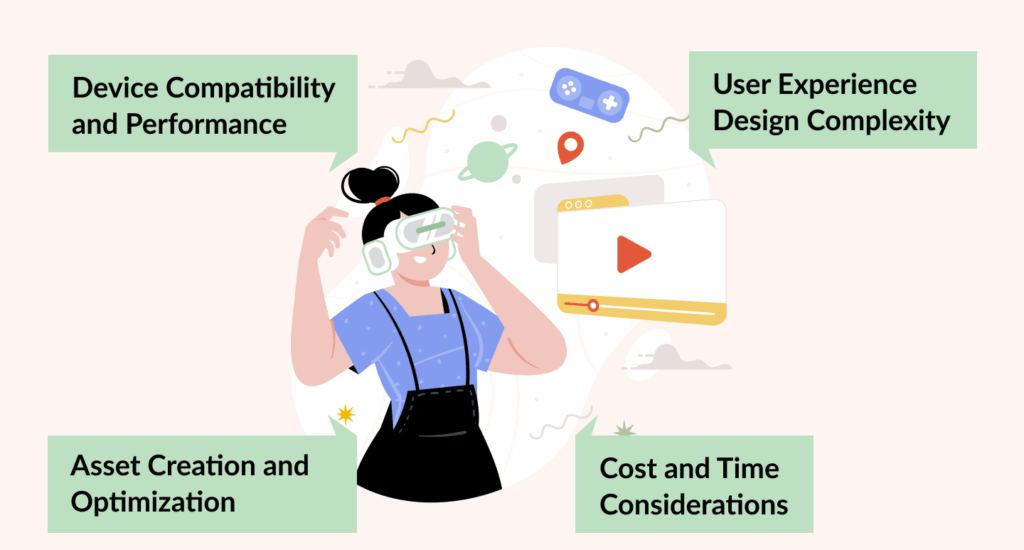
Obstacles in Interactive Augmented Reality Content Development
Interactive augmented reality certainly has outstanding engagement potential, but creating such experiences requires surmounting technical, creative, and operational hurdles. Awareness of these challenges allows better planning of businesses without wasting resources and to provide high-quality AR experiences that work across platforms.
Device Compatibility and Performance
Augmented reality content should work on a number of devices with multiple hardware capabilities, sensors, and processing power levels. Whereas one can expect most high-end mobile devices to perform well on complex AR visuals, mid-range devices may have limitations in rendering or tracking accuracy. Therefore, developers should be able to optimize assets, control file sizes, and manage frame rates to help deliver a seamless experience for every user.
Asset Creation and Optimization
Creation of the 3D models, textures, and animations takes a long time and skill for AR. Assets should, at the same time, not only appear real but also be lightweight enough for rendering in real time. Achieving this balance between quality and performance is often one of the largest bottlenecks in AR development, especially for large-scale environments and multiple interactive elements.
User Experience Design Complexity
In contrast to conventional applications or even websites, AR embraces that particular factor of spatial interaction. This is where the designers will have to consider how users move, view, and interact with the content in 3D space. While poorly designed interfaces may break immersion or even cause some degree of motion discomfort, UX teams must make sure that all layouts, gestures, and visual cues are cross-tested through different types of natural light and physical conditions in order to make intuitive control.
Cost and Time Considerations
In fact, making a fully interactive augmented reality experience calls for 3D artists, developers, and testers—perhaps, hence, making it resource-intensive. Custom animations, gesture tracking, and AI usually add considerable time and resource costs to such an experience. However, creating modular AR frameworks and using pre-built SDKs can quickly eliminate the much-dreaded development time while not eroding the truly novel part of such projects.
Nevertheless, most challenges faced by organizations continue to be offset by increased returns from AR investment. Production and appropriate quality investment in development typically lead to greater engagement, increased brand recall, and longer-term digital advantage.
Best Practices for Interactive AR Experiences
Creating an interactive augmented reality (AR) experience requires more than just having compelling imagery; it requires careful construction, optimization, and testing. Frequently, the most palpable AR experiences are those that seem intuitive, responsive, and significant to the user.
Optimizing 3D Assets for Performance
Heavy 3D assets slow down rendering, create lag, and most often behave as such on mobile devices. Models should be lightweight, textures compressed, and polygon counts kept low without being unappealing to the eye. Then employ the Level of Detail (LOD) technique so that an object looks sharp when viewed closely and simplified at will, which will benefit performance and provide comfort to the user.
Focus on Intuitive User Interface and Interactions
Discourse on AR interfaces being natural and simple would be bland. Clear visual cues, enabled by responsive gestures, should make it effortless for action to happen—perhaps tapping on an icon or rotating it in space and zooming in or out. There should be no skin, particularly the view of the user; the physical environment will still be blended into the experience. The right mix of things creates a feeling of control without instructions.
Test with Multiple Devices and Spaces
AR acts quite differently through lights, spaces, and devices; therefore, the experiences to be tested on both Android and iOS devices should be tested in bright and dim conditions, small places, and open spaces. The experience hosts stability and accurate tracking wherever the users engage with it.
Add Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Always be mindful that words such as “data” and “optimization” go side by side. You need to install proper AR analytics tools to discover how users interact with various components: what captures users’ attention, the time allocations they make, and what causes them to drop off. With these data, improvements can be made towards design, pacing, and interactions to boost engagement over time.
Necessary Combine Creativity With Purpose
All AR experiences must either educate, entertain, or sell. Do not get too complicated with effects or many other variables so far as the goal is concern. Best AR designs strike the balance between creativity and function, where technology pushes the story without overshadowing it.
Here in Esferasoft, we tailor these practices to design AR experiences that work well, captivate users, and improve day by day.
Cost and Time Estimates
At every stage – concept, 3D design, testing, optimization, and delivery – AR content is tailored to be interactive, with variations on cost and duration of delivery. Knowing this helps in planning prospective AR investments that are best for businesses in terms of quality, time, and scale.
Factors Affecting Price: Complexity, Features, Platform
The complexity of the experience is one of the major determinants for the costs involved in AR content development. For instance, a simple WebAR demo or filter would cost only simple dollars compared to a fully interactive AR app with complex gesture recognition integrated with AI and 3D animations.
Important pricing variables include:
- Type of AR experience: Marketing campaign, product visualization, or training simulation.
- Number of 3D models and animations required.
- Platform choice: mobile app, WebAR, or headset-based AR.
- Integration level with back-end systems or analytics dashboards.
The more interactivity a business seeks on the enterprise front, be it AI-based personalization or real-time data visualization, the higher the development cost can be expected. Still, such investments are generally worth their salt because they provide better engagement and ROI.
Typical Development Time (Simple vs. Complex AR content)
That’s precisely where you’re going to get the oddity with the timeframe since it solely depends on the scale of the project:
- Basic AR campaigns or filters: 2 to 4 weeks.
- Intermediate AR applications: 6 to 10 weeks.
- Advanced interactive AR platforms: 3 to 5 months, at times even longer.
The process entails conceptualizing, some 3D modeling, a little programming, UI/UX designing, and some testing on different devices. The collaboration of designers, developers, and QA teams must be very efficient to maintain the time schedule given without inhibiting work quality.
In-House vs. Outsourcing Options
Although some companies create internal AR teams, most brands prefer outsourcing for expertise, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By teaming up with a professional AR development company like Esferasoft, you can avoid the cost of in-house infrastructure while gaining access to advanced tools and certified developers working on much tighter deadlines.
TT Projects of AR well-planned are not just expenses; they represent strategic investments resulting in measurable engagement, conversion, and augmented branding.
If you want your estimated costs and timelines ready for AR development, get to Esferasoft; we help teams map, design, and deploy interactive AR solutions, according to the project budget, timeline, and overarching vision.

Future of Interactive AR Content
The future of interactive augmented reality content comprises intelligence, accessibility, and convergence. As technology forges ahead, AR is emancipating itself from the clutches of mobile apps, getting lighter and faster in its integration into daily devices and digital ecosystems. Businesses, educators, and creators are entering into a realm where augmented experiences are not just an event; they are ubiquitous.
WebAR and the Era of Cloud-Based AR
The next form of AR will be web-centric or designed for the Internet first. WebAR is a solution that shines in giving people access to ease of experience directly from the browser without any friction of downloading apps. Supported by cloud-based rendering, it presents high-quality visuals and interactions while remaining light on the device’s resources. Such a model is infinitely scalable, giving brands and companies opportunities to reach global audiences instantaneously.
AI-Generated Interactive Environments
Artificial intelligence is changing the paradigm of how augmented reality worlds are created. On-demand design of 3D assets and adaptive storylines that change according to the user’s actions will be achieved with augmented reality powered by AI to generate smarter and more personalized experiences. Future development of augmented reality environments will evolve and change according to the emotions, preferences, and even situations in which the user exists.
Integration with IoT and Smart Devices
With IoT devices and wearables finally going mainstream, AR will find its way into smart homes, automobiles, and workplaces. Fancy AR glasses diagnosing appliances and superimposing assembly instructions on a workbench? This merging of AR with IoT will redefine the very interaction paradigm that the physical world imposes upon end users.
Growth in AR Marketing and Gamification
Another trend that can be observed now is brands using AR for marketing purposes to create an emotional bond. The engagement of customers with newly developed interactive campaigns, AR scavenger hunts, and other types of gamified advertising will be added to the mix for further engagement. This demand for experiential content from AR by the younger, technology-savvy generation will play a significant role in shaping the interaction with and brand loyalty in the commercial world.
The development of AR is not just a matter of technology, but it is a matter of human behavior. The more natural, normal, and adaptive AR becomes, the better will be its smooth transition into everyday life.
Conclusion—Interactive AR: New Ways to Engage
Interactive content in augmented reality is changing the modes of connecting, learning, and purchasing people. It makes ordinary moments immersive experiences where the user is the activity participant instead of merely watching. From e-commerce to education and marketing to entertainment, companies adopting AR strategies are experiencing more enhanced engagement levels, stronger retention, and deeper emotional impacts with audiences.
The future will be experiences that feel personal, real, and responsive—interactive AR is just what delivers. By combining creativity and technology with AI, use will enable brands to outsell the static experience and design environments that respond uniquely to each user.
At Esferasoft, we help businesses bring the AR content creation and engagement solutions to provide the much-needed differentiation in a highly interconnected world. Transform how your audience interacts with your brand—through innovation that actually engages. To learn more, call now at +91 772-3000-038!
FAQ’s
1. What is interactive AR content?
Interactive AR refers to instances whereby users get to interact directly with digital featurettes placed within the real-world settings. This interaction could be through touch, rotation, movement, gesture or voice commands, or any motion. It integrates 3D modeling, tracking, and real-time interaction to give personalized and very engaging experiences.
2. How is interactive AR different from general AR?
General AR often imposes the digital object on the environment of the physical world without altering user control. General AR is primarily visual. However, interactive AR allows an interaction established by the user’s actions. For example, one does not merely look at the product model but also changes colors, explores features, and fires animations by various gestures or simply touch.
3. Is it being beneficial for which industry?
The majority of retail, education, real estate, games, manufacturing, and marketing industries are harnessing interactive AR. Retailers use it for virtual try-ons, educators for immersive learning, architects for virtual walk-throughs, and marketers for interactive campaigns that increase engagement and brand recall.
4. What tools are used to create interactive AR content?
Various 3D design tools Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max; game engines Unity or Unreal Engine; and AR SDKs ARKit, ARCore, and Vuforia are used by developers. All combine to permit essentially real-time rendering, motion tracking, and environment mapping, with the aim of providing AR that is as smooth and realistic as possible.
5. Does AI enhance experience in interactive AR?
Definitely. AI improves AR to become smarter and more personalized. This ensures the real-time analysis of user behavior with the dynamic adaptation of content and automatic generation of 3D assets. It recommends all those predictive analytics for private optimization in engagement; it is going to be proof of gesture recognition as well as voice command and the object it recognizes, thus making AR very intuitive.
6. Does an interactive AR experience take more like two days?
It depends on project complexity. Simple AR filters can be delivered in 2 to 4 weeks, whereas a fully interactive app complete with 3D assets, AI functionalities, and cross-platform compatibility could take anywhere between 2 and 5 months. The design form, targeted platform, and testing requirements are just some of the factors that could contribute to this variability.
7. How much does the development of interactive AR content generally cost?
Costs may vary according to the size of the application and the services used. A basic AR campaign might begin with $5,000 to $10,000, whereas enterprise-wide AR apps often reach the $50,000 to $100,000 range. The following are determining components: asset quality, platform choice (mobile, WebAR, and headset launching) of AI, and relationship to analytics tools.
8. Are interactive AR experiences compatible with mobile devices?
Yes. Most AR experiences are meant for today’s smartphones and tablets. The technologies, ARCore (Android) and ARKit (iOS), ensure perfect tracking and rendering. WebAR makes the viewing easier since it enables the users to experience AR from their browsers without having to download any applications.
9. Can interactive AR content be added to websites or apps?
Certainly. With such innovations in AR, companies can weave them into their individual sites: e-commerce portals or mobile applications. When integrated with WebAR or an SDK, users will, through virtual try-on demos or product view demos, be able to interact directly with the 3-D model through pages or application interfaces.
10. What are the trends that will shape the future of interactive AR content?
Among the important pillars for future interactive AR content are WebAR, AI-powered personalization, cloud rendering, and interfacing with other IoT devices and intelligent appliances. This has been the good harmonization of progress in which AR hardware and software make augmented realities increasingly available, adaptable, and connected to daily life.